← Back to Topics
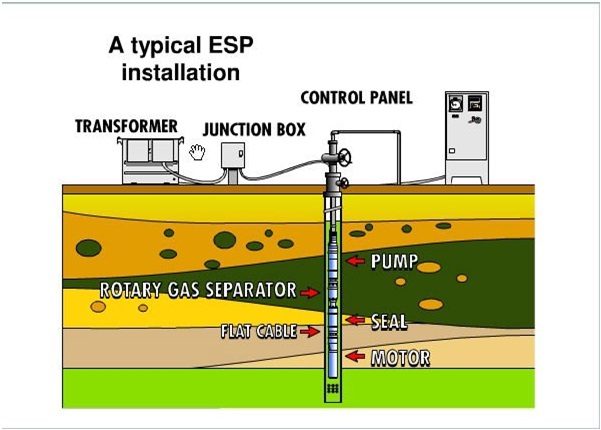

ESP Design – Hand Calculations guide
Production-Surveillance-Intervention — Artificial Lift
The ESP Design – Hand Calculations guide provides a step-by-step walkthrough for designing an Electrical Submersible Pump (ESP) system, especially useful for wells producing water and light crude oil. Here's a summary of the 9-step design procedure:
🧩 1. Basic Data Collection
Well profile, casing, tubing, perforation depth
Fluid properties: API gravity, water cut, GOR, pressures, temperatures
Production targets and power availability
📈 2. Production Capacity
Uses Productivity Index (PI) to estimate inflow performance
Calculates flowing bottomhole pressure (Pwf) and pump intake pressure (PIP)
💨 3. Gas Calculations
Determines free gas volume at pump intake
Uses Standing’s correlation for solution GOR
Calculates oil and gas formation volume factors (Bo and Bg)
📏 4. Total Dynamic Head (TDH)
Combines net well lift, tubing friction loss, and wellhead pressure head
Uses Hazen-Williams formula for friction loss
🔄 5. Pump Type Selection
Chooses pump series based on casing size and flow rate
Calculates number of stages and required brake horsepower (BHP)
⚙️ 6. Compound Sizing
Selects seal, motor, and evaluates gas separator need
Motor selection considers frequent starts/stops and voltage requirements
🔌 7. Cable Selection
Determines cable size, type, and length
Calculates voltage drop and power loss for cost analysis
🛠️ 8. Accessory Equipment
Includes motor lead extension, cable bands, protectors, check valves
Surface equipment like Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) and transformer taps
📊 9. Final System Integration
Ensures all components are compatible and optimized for performance and cost.
ESP Design Form is here

🧩 1. Basic Data Collection
Well profile, casing, tubing, perforation depth
Fluid properties: API gravity, water cut, GOR, pressures, temperatures
Production targets and power availability
📈 2. Production Capacity
Uses Productivity Index (PI) to estimate inflow performance
Calculates flowing bottomhole pressure (Pwf) and pump intake pressure (PIP)
💨 3. Gas Calculations
Determines free gas volume at pump intake
Uses Standing’s correlation for solution GOR
Calculates oil and gas formation volume factors (Bo and Bg)
📏 4. Total Dynamic Head (TDH)
Combines net well lift, tubing friction loss, and wellhead pressure head
Uses Hazen-Williams formula for friction loss
🔄 5. Pump Type Selection
Chooses pump series based on casing size and flow rate
Calculates number of stages and required brake horsepower (BHP)
⚙️ 6. Compound Sizing
Selects seal, motor, and evaluates gas separator need
Motor selection considers frequent starts/stops and voltage requirements
🔌 7. Cable Selection
Determines cable size, type, and length
Calculates voltage drop and power loss for cost analysis
🛠️ 8. Accessory Equipment
Includes motor lead extension, cable bands, protectors, check valves
Surface equipment like Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) and transformer taps
📊 9. Final System Integration
Ensures all components are compatible and optimized for performance and cost.
ESP Design Form is here

💬 Comments
✍️ Leave a Comment